Let’s discuss the question: how do hydrogen bonds compare with other intermolecular forces apex. We summarize all relevant answers in section Q&A of website Abettes-culinary.com in category: MMO. See more related questions in the comments below.
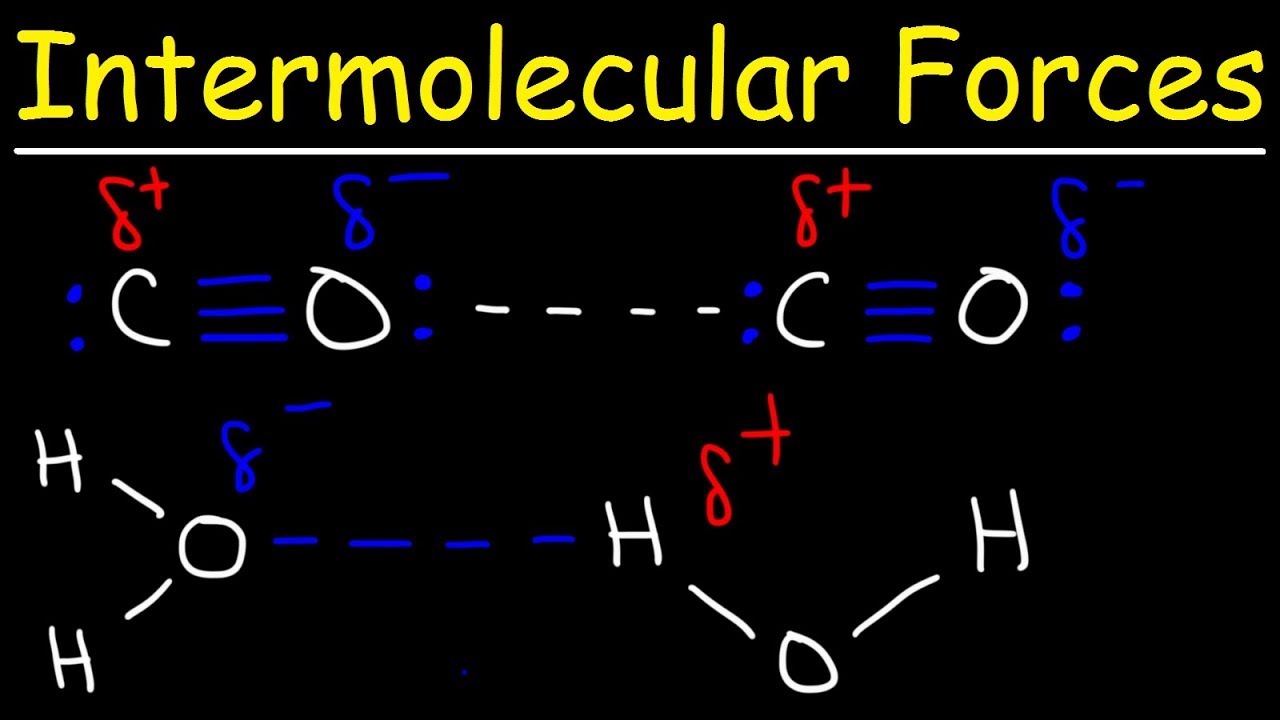
How does hydrogen bonds compare with other intermolecular forces?
Hydrogen bonds are are generally stronger than ordinary dipole-dipole and dispersion forces, but weaker than true covalent and ionic bonds.
Which is stronger intermolecular forces or hydrogen bonding?
Hydrogen bonds are a special case of dipole-dipole interactions. H-bonds are the strongest intermolecular force. (They are worth ca.
Intermolecular Forces – Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole Dipole Interactions – Boiling Point \u0026 Solubility
[su_youtube url=”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XSRa9P-xJl0″]
Images related to the topicIntermolecular Forces – Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole Dipole Interactions – Boiling Point \u0026 Solubility

Why are hydrogen bonds the strongest of the intermolecular forces?
Hydrogen bonds are strong intermolecular forces created when a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom approaches a nearby electronegative atom. Greater electronegativity of the hydrogen bond acceptor will lead to an increase in hydrogen-bond strength.
Do hydrogen bonds have high intermolecular forces?
…
How forces of attraction affect properties of compounds.
| Type of compound | Intermolecular forces present | Relative order of boiling and melting points |
|---|---|---|
| Covalent compounds containing hydrogen bonds | Hydrogen bonds, London dispersion forces | 2 |
Is hydrogen bonding a dispersion force?
The three major types of intermolecular interactions are dipole–dipole interactions, London dispersion forces (these two are often referred to collectively as van der Waals forces), and hydrogen bonds.
Are hydrogen bonds stronger than dipole-dipole?
Hydrogen bonds are typically stronger than other dipole-dipole forces.
How do typical dipole-dipole forces differ from hydrogen bonding in what way are they similar?
Typical dipole-dipole forces are strong bonds between atoms, some of them usually quite electronegative. Hydrogen Bonding is between molecules and is a weak bond that usually requires the presence of hydrogen.
What is the strongest type of intermolecular force present in h2?
The strongest intermolecular force is hydrogen bonding, which is a particular subset of dipole-dipole interactions that occur when a hydrogen is in close proximity (bound to) a highly electronegative element (namely oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine).
What’s the difference between dipole and hydrogen bonding?
An ion-dipole force is a force between an ion and a polar molecule. A hydrogen bond is a dipole-dipole force and is an attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen on one molecule and a slightly negative atom on another molecule.
Intermolecular Forces – Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole-Dipole, Ion-Dipole, London Dispersion Interactions
[su_youtube url=”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QdwzMPwPA3I”]
Images related to the topicIntermolecular Forces – Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole-Dipole, Ion-Dipole, London Dispersion Interactions

Why is hydrogen bonding so strong in comparison with other dipole-dipole interactions?
Because a hydrogen atom is so small, these dipoles can also approach one another more closely than most other dipoles. The combination of large bond dipoles and short dipole–dipole distances results in very strong dipole–dipole interactions called hydrogen bonds, as shown for ice in Figure 12.8.
What kind of bonds are hydrogen bonds apex?
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules, not a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom. It results from the attractive force between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as a N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom.
How covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds are similar?
Similarities Between Covalent and Hydrogen Bonds
Covalent and hydrogen bonds are types of chemical bonds. Both types of bonds occur between two atoms. Both types of bonds act as a glue between two atoms.
Is there hydrogen bonding in H2?
Answer and Explanation: H2 is not a hydrogen bond but is a molecule in which hydrogen is bonded to itself. H2 forms when two hydrogen atoms, H, are bonded together by a… See full answer below.
Are hydrogen bonds strong or weak?
Hydrogen bonds are a strong type of dipole-dipole interaction. As a Rule of Thumb, they are weaker than covalent and ionic (“intramolecular”) bonds”, but stronger than most dipole-dipole interactions. There are two requirements for hydrogen bonding.
What does a hydrogen atom need to be in for hydrogen bonding to occur?
hydrogen bonding, interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity for electrons; such a bond is weaker than an ionic bond or covalent bond but stronger than van der Waals forces.
What intermolecular forces are present in gaseous hydrogen?
This is the attraction between one slightly positive and one negative jobs here. So if we see for the correct answer, the inter molecular forces which are present in the gaseous hydrogen, our di pole dipole interaction. So this is the final answer of discussion.
How are hydrogen bonding forces formed?
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole interaction that occurs between the lone pair of a highly electronegative atom (typically N, O, or F) and the hydrogen atom in a N–H, O–H, or F–H bond.
Hydrogen Bonds In Water Explained – Intermolecular Forces
[su_youtube url=”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZDjJOqOKeCI”]
Images related to the topicHydrogen Bonds In Water Explained – Intermolecular Forces
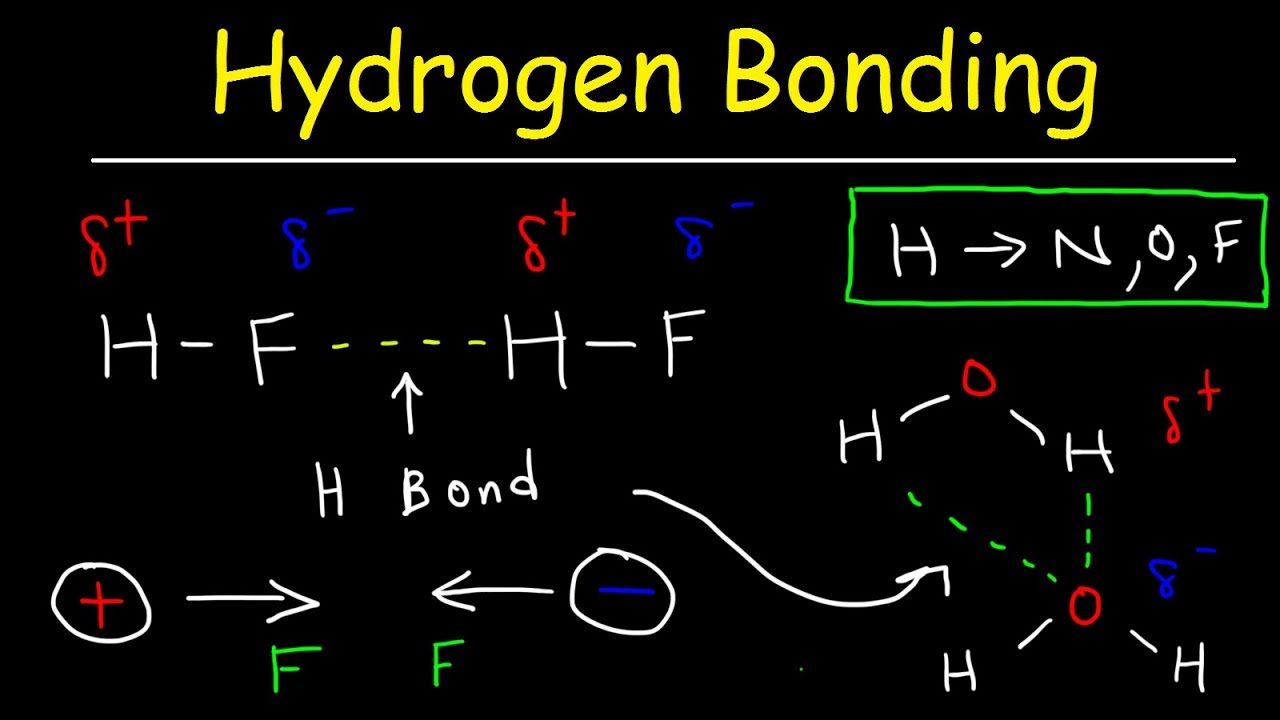
How are dipole-dipole attractions London dispersion forces and hydrogen bonding similar?
How are dipole-dipole attractions, London dispersion forces, and hydrogen bonding similar? They are all forces of attraction between molecules. In all cases there is an attraction between the slightly negatively-charged portion of one molecule and the slightly positively charged portion of another molecule.
How does ion-dipole forces differ from dipole-dipole forces?
Ion-dipole forces are stronger than dipole interactions because the charge of any ion is much greater than the charge of a dipole; the strength of the ion-dipole force is proportionate to ion charge. Ion-dipole bonding is also stronger than hydrogen bonding.
Related searches
- which sentence best describes the bonding shown
- what is an energy sublevel
- which term describes this molecular shape
- in which situation would dipole dipole forces be significant
- which molecule can form hydrogen bonds with others like it
- what is a molecular dipole moment
- what is required for two atoms to share electrons equally in a chemical bond apex
- what determines the strength of a dipole dipole force
- how should you indicate that there are multiple polyatomic ions in a chemical formula
- what determines the strength of a dipole-dipole force
Information related to the topic how do hydrogen bonds compare with other intermolecular forces apex
Here are the search results of the thread how do hydrogen bonds compare with other intermolecular forces apex from Bing. You can read more if you want.
You have just come across an article on the topic how do hydrogen bonds compare with other intermolecular forces apex. If you found this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much.